CB2 Receptor – Chronic pain is a widespread and debilitating condition that can seriously affect the patient’s quality of life. Research in recent years has identified that endocannabinoids have significant analgesic properties, which is a breakthrough in providing neuropathic pain relief.
However, little research has been conducted on intra-neuronal CB2 receptors to understand their role in reducing chronic pain and whether they can be used as therapeutic targets for chronic pain management.
This article aims to provide the reader with a comprehensive overview of the role of cannabinoid receptors in the nervous system.
Table of Contents
What is A CB2 Receptor?
It is a G-protein coupled receptor expressed primarily on immune cells, but it can also be found on neuronal tissues. Its stimulation by endogenous or exogenous cannabinoids has been shown to have immunomodulatory effects.
CB2 receptors can control the expression of genes encoding for various proteins involved in cytokine regulation, inflammatory response, and pain control. CB2 receptor activation can also reduce the release of eicosanoids, neuropeptides, and proteolytic enzymes.
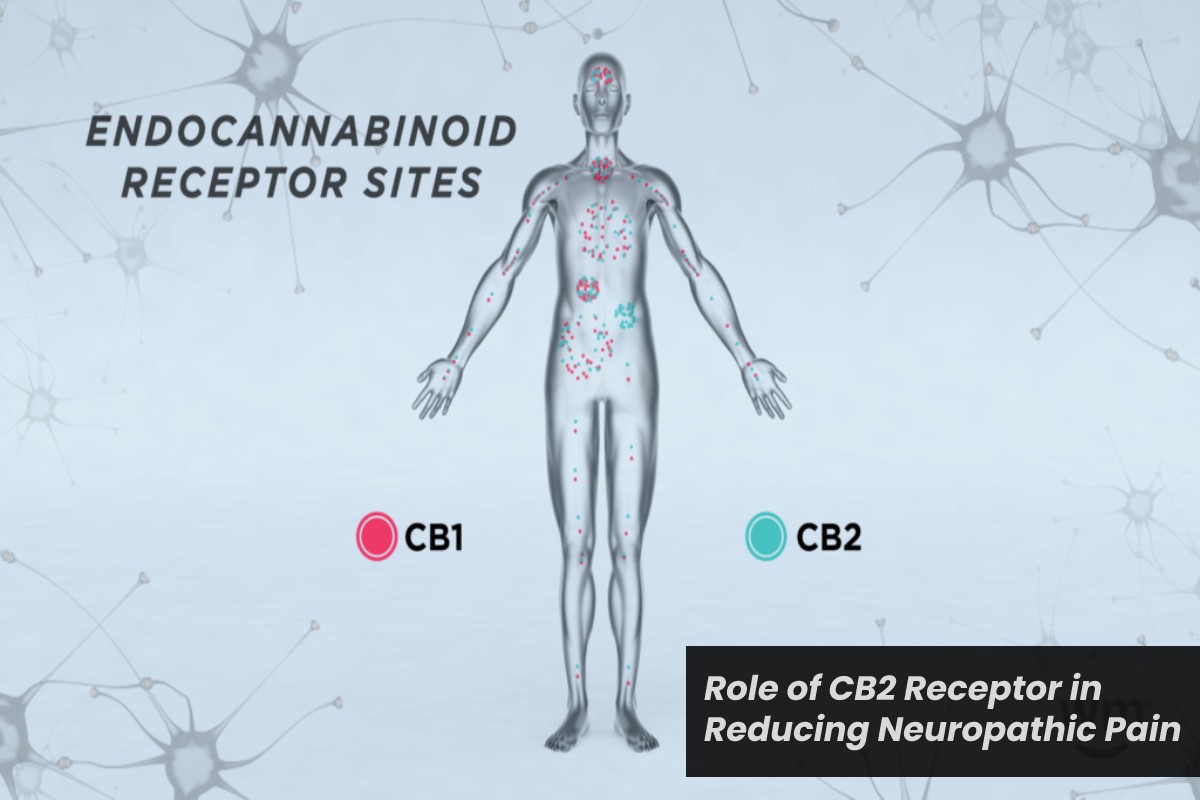
CB1 versus CB2
CB1 receptors are present in almost all brain regions. They mediate most of the psychoactive properties of cannabinoids in the CNS, such as sedation, hypothermia, analgesia, and memory enhancement. CB2 receptors are expressed mainly on immune tissues and neurons in the peripheral nervous system.
These receptors are much less famous than their cousins CB1, and studies have shown that they only contribute to a fraction of the current knowledge on cannabinoids. However, the investigation has indicated that these receptors play a significant role in modulating encephalomimetic pathways.
Several studies have demonstrated that the blockade of the CB2 receptor could increase the evoked N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) response and increase spine density. These results suggest the potential involvement of CB2 receptors in the modulation of neuronal excitability.
Cannabinoids in Animal Models of Pain
CBD oil can be used in any recipe so your dog can receive the benefits without you having to cook with it. A recent study has shown that cannabinoids effectively reduce neuropathic pain in animals models of chronic pain.
CBD oil tinctures like the ones offered at cbdMD have shown a significant reduction in neuropathic pain in rats. These results demonstrated that cannabinoids reduce the pain-related hyperalgesia and allodynia caused by nerve injury. Furthermore, cannabinoid administration can provide effective pain relief but while it provides no analgesic effects by itself.
Clinical Trials of Cannabis/Cannabinoids in Chronic Pain
Research studies on cannabinoids have demonstrated that these compounds have the potential to reduce chronic pain. Various cannabinoid preparations have been administered to animals with chronic pain.
However, the development of appropriate clinical studies has been hampered by the lack of adequate dosages and delivery systems, such as the oral route. The first clinical trial in this area (known as Sativex) was initiated in 2006 in Canada.
It is a clinical trial involving post-herpetic neuralgia patients, which revealed significant improvements in pain symptoms and quality of life. Cannabis has also been examined for its therapeutic potential as a treatment of neuropathic pain in multiple sclerosis.
However, this trial found that cannabis did not provide any significant benefit against the loss of function associated with the disease.
The discovery that endocannabinoids have pain-relieving effects has provided a new therapeutic avenue for treating chronic pain. The use of cannabinoid agonists and antagonists in animals has revealed the therapeutic potential of these agents for the management of neuropathic pain conditions.
However, more studies are needed to identify optimal dosages and delivery systems before cannabinoid therapies can be implemented clinically.