Table of Contents
Vitamin B2(Riboflavin) Definition
Vitamin B2 or riboflavin is a water-soluble vitamin necessary for energy production. B 2 supplements generally find as part of a multivitamin formula or B vitamins.
Vitamin B2 finds in the human body as part of coenzymes. The biologically active forms are FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) and FMN (flavin mononucleotide).
These nucleotides participate in many metabolic processes in the body, including some vitally essential functions in aerobic metabolism and eliminating toxins.
What are the Properties of Vitamin B2?

- Vitamin B2 also influences the human body’s antioxidant capacity since different enzymes, such as glutathione reductase, require its presence to act correctly.
- Riboflavin-deficient diets result in increased cardiovascular risk. Vitamin B2 deficiency can also affect iron metabolism, increasing the risk of anemia.
- Its deficiency has links to chapped lips, dry skin, tearing and red eyes, anemia, sensitivity to light, carpal tunnel syndrome, leg swelling, cataracts, fatigue or weakness, depression, migraines, shortness of breath, stress, or depression.
- People most at risk of deficiencies are pregnant women, infants, children, the elderly, and athletes. The consumption of contraceptives, antidepressants, alcohol, anticancer drugs, or antibiotics increases your requirements.
- Vitamin B2 deficiency interferes with the activity of other nutrients, especially other B vitamins, such as vitamin B9, vitamin B3, vitamin B12, and vitamin B6.
- Other foods such as meat, fish, organ meats, eggs, and shellfish are also considered good riboflavin sources.
- Among plant foods, foods such as peas, beans, green leafy vegetables, nuts, wild rice, brewer’s yeast, and Nori algae also contain this vitamin. Vitamin B2 quickly destroys by light, especially direct sunlight.
What are the Benefits of Vitamin B2?

- Vitamins of group B riboflavin It is of vegetable origin and cannot be synthesized in animals.
- Its use in the prevention of cataracts and many diseases. Riboflavin plays an essential role in fat metabolism.
- It helps the formation of energy and respiration in the cell, is particularly compatible with oxygen in tissues such as skin, hair, and nails.
- It was playing an essential role in growth and development. Riboflavin In animal experiments showing the lack of growth and development of the subjects first stopped.
- Önemli Important for the metabolism of foods with thiamine and niacin, It is a water-soluble vitamin.
- Flavoprotein, which acts as a coenzyme for normal energy metabolism, activates vitamin B6 and converts niacin to the form that the body can use.
- Food with riboflavin should not keep in the light because it is sensitive to light. The cooking water of vegetables and yogurt juice should not spill as it is a water-soluble vitamin.
- Riboflavin is a regulator involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and lard is one of the B vitamins.
- It is a necessary vitamin to take with food. Deficiencies in
- Wounds occur on the skin (dermatitis), lips (keyless, angular lesion), and cut wounds around the eyes.
- Nervous system disorder, anemia.
- Burns and red eyes can cause diarrhea.
10. As a result of not getting enough niacin in the diet, pellagra disease occurs with symmetrical wounds in the nervous system, digestive system, and sun-exposed skin.
Food Sources of Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2 is essential for its host of health benefits and water-soluble vitamin. It is carried through the bloodstream and gets easily eliminated from the body via urine.
Hence one must always keep up the intake of natural foods containing riboflavin to alleviate deficiency syndromes. Although most vitamin B2 comes from milk and other dairy products, the markets also flood with other dietary items rich in this vitamin.
The most prominent sources of vitamin B2 are:
1. Milk, Cheese, and Other Dairy Products

- Vegetables include beans, broccoli, mushrooms, avocados, dried peas, Brussels sprouts, soybeans, sea vegetables, green peas, bell peppers, sweet potato.
- And dark green leafy vegetables, such as asparagus, collard greens, turnip green, mustard green, celery, romaine lettuce, and spinach.
2. Fresh Fruits

- Seeds and grains include millet, sunflower seeds, wheat germ, wild rice, whole grains, wild rice. Fortified foods include bread, baby foods, breakfast cereals, pasta, and whole-grain products.
- Animal sources include salmon, mackerel, eel, sardines, meat, and poultry, such as chicken, turkey, kidneys, and liver.
- Vitamin B2 is also present in minute quantities in apples, figs, carrots, and cabbages. Unlike other vitamins, the B2 vitamin does not get destroyed or eliminated while cooking.
- Hence most of the food under this category can easily enjoy as a delicious dish.
Deficiencies of Vitamin B2
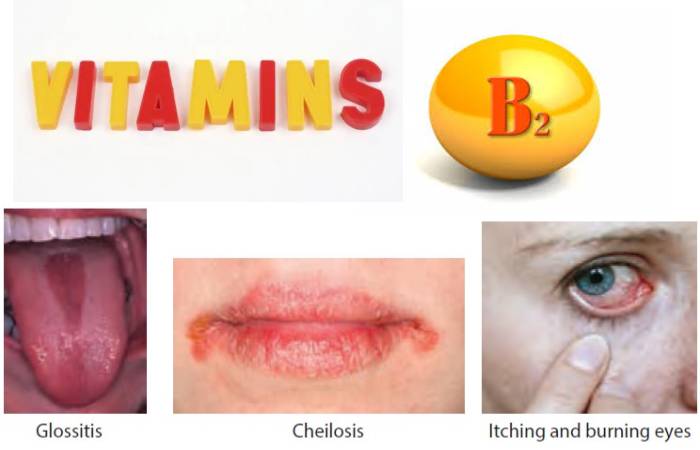
- This vitamin is essential for providing energy to the body for carrying various activities. Lack of it can decrease the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, leading to underlying deficiency syndromes.
- Riboflavin deficiency causes stomatitis, including a painful red tongue with a sore throat, red chapped, and fissured lips (also called cheilosis).
- And inflammation of the corners of the mouth, inflammation of the tongue, mouth ulcers, and cracks at the corner of the mouth (i.e., angular cheilitis).
- Generally, a diet lacking this potent nutrient may cause bloodshot eyes, high sensitivity to light, a burning sensation in the eyes or itchy, watery eyes, split nails, dry or oily hair, dandruff, indigestion, dizziness, insomnia, etc.
- Lack of riboflavin in the diet causes malfunctioning of the adrenal glands leading to conditions like anemia, cataract, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
- It can also lead to scaly skin rashes on the male and female genitals, rashes on the upper lip’s medial aperture, or the smile lines connecting the nose and chin (i.e., nasolabial fold).
- A diet deficient in this B vitamin for a pregnant woman can also cause congenital disabilities, congenital cardiac defects, abnormal limbs, and deformities in the fetus. It can also lead to pellagra or malaria in adults.
- If the symptoms of riboflavin deficiencies do not meet with an extended period, it may also lead to the liver and neural system’s degeneration.
Toxicity of Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B2 is one such essential nutrient that does not portray any abnormal side effects or contraindications if taken in an optimum amount.
- A diet rich in riboflavin mostly turns the color of urine yellowish-orange.
- The Food and Nutrition Board for the National Institute of Medicine vouches for this vitamin’s safety in children after proper consultation with a nutritionist.
- The Recommended Daily Allowance of the B vitamin is 1.3 mg daily for men and 1.1 mg for women.
- It is essential to consult a doctor or health supervisor before taking Vitamin B2 in supplement form.
- An overdosage might cause migraine, cataract, stomach pain, diarrhea, and increased urine.
Applications of Vitamin B2
- The external contribution of riboflavin seeks to guarantee the requirements of this vitamin and thus avoid its deficiency.
- Dietary supplements with vitamin B2 help protect the mucous membranes. They also minimize the damage caused by stress and exercise, protecting the nervous system.
- B2 supplementation reduces homocysteine levels. This substance in high amounts is related to an increase in cardiovascular risk. It can also help prevent cataracts or treat migraines.
- Athletes have higher requirements for this and other B vitamins, so it may be convenient to supplement this vitamin’s diet.
Doses of Vitamin B2
- The RDA is 1.3 mg for men and 1.1 mg for women. However, the recommendation for the Spanish population is 1.6 mg.
- There are certain circumstances in which the requirements may increase, and it may be advisable to consume higher doses.
- It is not advisable to consume quantities more significant than 20 mg of B2 in a single dose because the body cannot use more than that amount. The excess is eliminated in the urine, giving urine a “fluorescent” color.
- Riboflavin supplementation is most effective when taken with food and in a multivitamin formula.
Precautions of Vitamin B2
- Riboflavin is generally considered safe even in high doses. Its toxicity is rare, but very high doses can cause itching, numbness, burning sensation, and sensitivity to light.
- Side effects generally found in amounts greater than 100 mg. However, it has been observed that doses from 10 mg can generate photosensitivity, and it recommends protecting yourself with sunglasses.
- High doses can reduce the activity of some medications, such as those used to treat cancer, antibiotics, or some antidepressants.
- For this reason, it is advisable to consult a specialist if you are taking medication before consuming large doses of riboflavin.
Conclusion
Vitamin B2 is a water-soluble nutrient essential for breaking down fats and carbohydrates into simpler forms to enrich the body with a dose of energy for carrying out the various bodily functions.
Being a potent antioxidant, it holds high significance in treating many ailments, including anemia, migraine, heart problems, vision disorders, liver problems, and is extremely beneficial for healthy skin and hair.
Blessed with a good load of dietary options, one can easily avoid the deficiency syndromes and reap the benefits.

